In the new version of CMS 4media dedicated to local media, special SEO fields have been designed.
Thanks to them, editors and journalists have greater control over how indexed URL addresses can appear in the Google search engine.
Where can you find the SEO fields in CMS 4media?
The SEO fields are available for content published in the following modules:
- Articles
- Authors
- Subpages
- Events
- Photo galleries
- Multimedia
- Business Directory
- Classifieds
Additionally, in the general settings, you can find "SEO Settings," which allows you to enable/disable site indexing (disabling means that the site won't be visible in Google search engine results) and set the title and description of the page in the search engine.
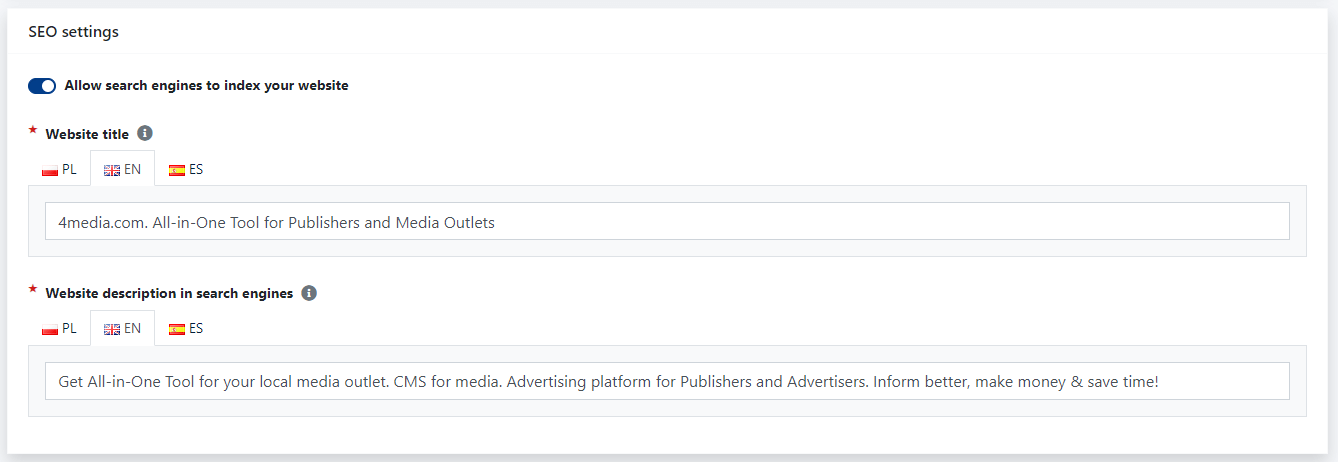
What elements do the SEO fields consist of?
The SEO fields consist of the following elements in CMS 4media:
- Title,
- Description,
- Indexing,
- Canonical URL,
- Google Preview
- Social media photo.
SEO Title
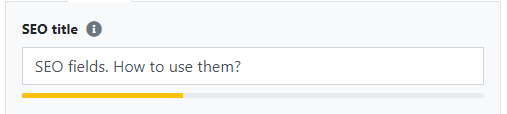
By default, when writing content in the text editor, the SEO title field is automatically filled in.
This doesn't mean that the CMS system itself selects a title that will have "greater SEO power". We can leave it unchanged, in which case it will be the same as the editorial title of our article or subpage (and this is not an error).
The SEO title is the one that will be visible in the search results on Google.
The SEO title can have a maximum of 80 characters including spaces. To choose the appropriate title length, a character counter is provided, which shows the number of characters used in real-time, along with a visual indicator.
The visual indicator helps quickly determine the appropriate length for the SEO title based on three colors:
- Yellow: the title may be too short.
- Green: the title length is appropriate.
- Red: the title is too long and may be cut off in search results.
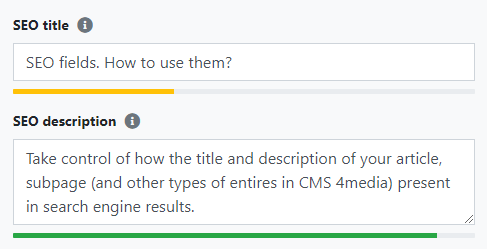
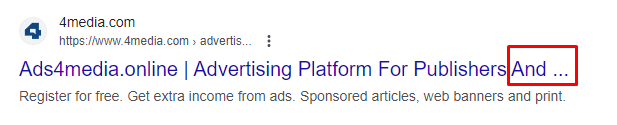
ATTENTION! If the SEO title exceeds 80 characters, it will be shortened. Therefore, be careful when pasting longer titles and make sure that the last word is not cut off (as shown in the image below).
SEO description
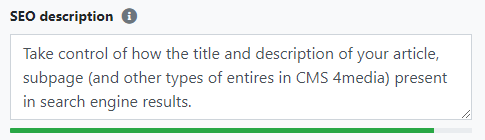
The SEO description (meta description) is the page description visible in the search engine. It is a longer text snippet that appears directly below the page SEO title on the search results list.
It is in the meta description tag that you should place a unique description of the page. This summary of the website's content is meant to encourage users to click.
The meta description only appears on the search results list and is invisible after accessing the page.
When writing an article, by default, in CMS 4media, the SEO description field remains empty. Nothing will happen if you don't fill it in. Google will select a text snippet from the page and display it in the search engine results as the page description in relation to the user's query. This doesn't mean, of course, that this description will be automatically filled in CMS.
In practice, Google can display a different description to each user. The algorithm will strive to display a text snippet from the page that best matches the query entered by the user in the search engine.
If you’d like to have greater control over this and increase your chances of having Google display the same description to every user, it's worth filling in the SEO description manually.
The SEO description in CMS 4media can have a maximum of 160 characters, including spaces.
Just like with the SEO title, the character counter provides real-time guidance for choosing the appropriate description length, along with a visual indicator.
The visual indicator assists in quickly determining the suitable SEO description length using three colors:
- Yellow: The description may be too short.
- Green: The description length is appropriate.
- Red: The description is too long and might be truncated in search results.
Indexing by search engines
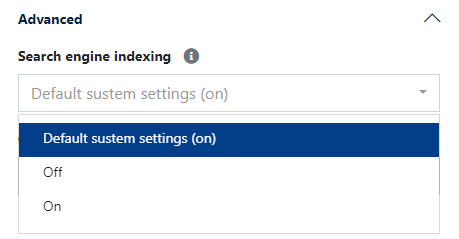
After clicking on the "Advanced" options, a SEO field related to indexing specific articles or subpages appears.
From the dropdown menu, you have three options to choose from:
- Default system settings (recommended) - set by default; this means that the content will or will not be indexed based on what is specified in the "SEO Settings" under "Settings".
- Disabled - indexing of specific content is prohibited for indexing robots.
- Enabled - indexing of specific content is allowed for indexing robots.
NOTE: If you have indexing disabled in the general SEO settings (slider moved to the left), but during editing, for example, an article, you set indexing to "Enabled" in the SEO fields - the changes will overwrite the global settings of the webpage. The specific article will be accessible to Google robots, which can add that particular subpage to the search results list.
In other words, the article will then be indexed and visible to users on Google.
Canonical URL
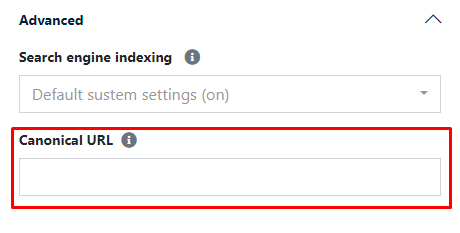
This SEO field is also located in the advanced options.
The canonical URL is a tag that instructs Google's robots which link on a webpage is the original one, i.e., where the original content resides (or which page is most important to us - the one for which we want to build the best visibility on Google).
Canonical URLs play a crucial role in page indexing, as they protect against what is known as "duplicate content."
Google preview
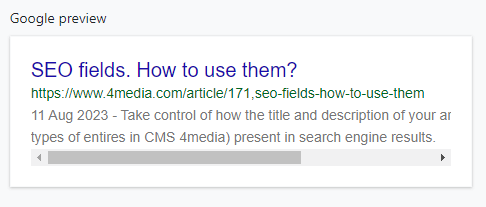
In the box labeled "Google Preview," there is a real-time updating simulator of how a specific subpage or article will might appear in Google search results. The preview is generated for the desktop view, meaning desktop computers or laptops.
It provides a glimpse of how an article, for example, will look after filling in the SEO fields for the title and description, along with the URL address.
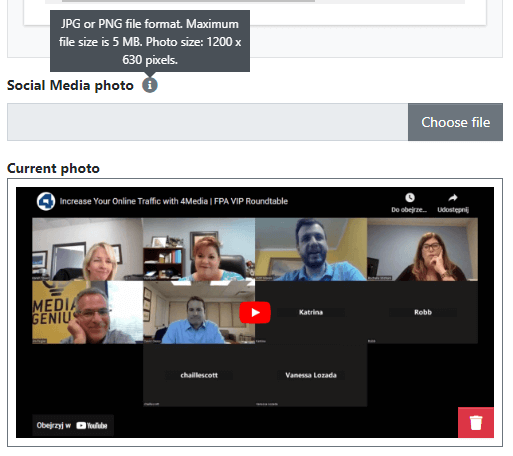
Image for Social Media
In this section, you can select an image or graphic from your computer's storage, which will be visible as a thumbnail for an article/link on social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, or LinkedIn.
Click the "Choose File" button to select an image or graphic from your computer. It should be a PNG or JPG file with exact dimensions of 1200 x 630 pixels and a file size no larger than 5 MB.
After uploading the image, click the "Save" button at the bottom of the page to save the changes. After this action, upon reloading the page, you will see the current image displayed on social media.
More about images in Social Media and checking link previews can be found in the guide: SEO fields - Social media photo.
Best practices
It is worth creating separate titles - editorial and SEO - for each article.
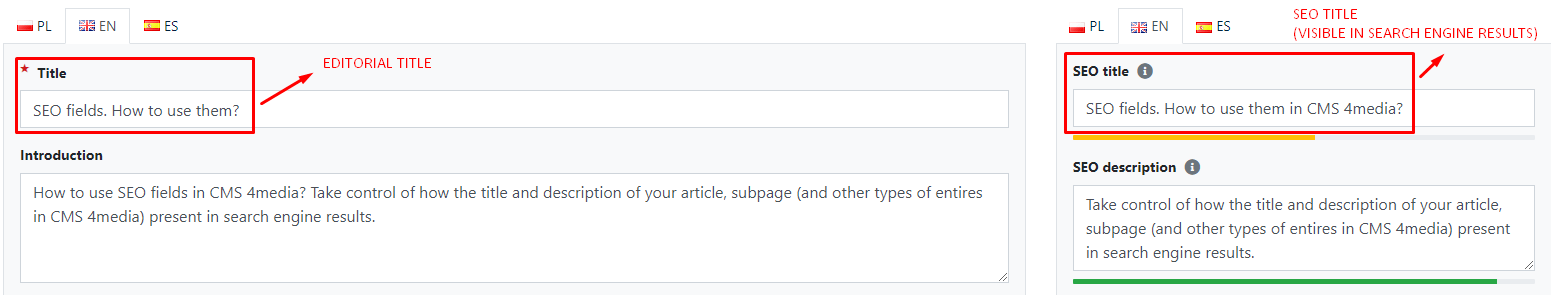
The editorial title is important from the perspective of services like Google News and Google Discover. Their construction should be different because these headlines are analyzed and fetched by indexing robots of the mentioned services. Editorial titles appear as headlines for press releases published in these services.
The SEO title should be created with the user in mind, who is searching for something in a search engine - not browsing news in the Google Discover and Google News sections, but rather opening Google's browser because they want to find something or learn more about a particular topic.
Therefore, they have a different intention with which they navigate the internet.
People who need more control over the appearance of the title and description of articles or subpages in search results can use a tool: https://mangools.com/free-seo-tools/serp-simulator.
The simulator shows how the title and description for a given content might appear on computers and smartphones. This allows for even more precise optimization of elements like keywords and language of benefits, ensuring that the main message is always visible at the beginning of the title or description on both mobile and desktop devices.
I entered my title in the SEO fields, but Google is displaying something different! What's happening, what to do, how to live?!
In August and September 2021, a Google update occurred in the way web titles are generated.
So, how can titles be created currently? Google explains it as follows:
We particularly use the text that users see when they open a website. We consider the main title or heading visible on the page, the content often placed by site owners in <H1> tags or other header tags, as well as text that is large and well-visible due to style tags.
We can also take into account the text on the page and in the links leading to it.
In practice, the title entered in the SEO title field in CMS 4media may not always appear in search results. It can be replaced by the first-level H1 header (the content entered as the article title in CMS 4media) or other content that Google deems appropriate.
Of course, only Google's algorithm evaluation determines which title will actually be displayed.
To increase the chances of displaying the title in the desired form, you need to:
- Avoid creating very long titles - it's better to stick to a specific, concise, non-misleading title.
- Avoid creating titles stuffed with keywords, e.g., "Football. Football news site. Soccer updates."
- Avoid generic and uninformative titles like Homepage, Untitled - repeated multiple times on the website pages.
- Avoid empty <title> tags.
Additional sources of information:
