Table of contents:
- What is Google Trends?
- How to use Google Trends?
- Seasonal trends in Google Trends
- The importance of regional language in Google Trends
- How to use Google Trends in a journalist's work?
- Summary
If you are an online publisher or owner of a news website, you have surely come across the phrase ‘Google Trends’ more than once. Since you’re reading this article, you probably sensed that it could be useful to you. And rightly so! This article will teach you how to use Google Trends to increase the reach of your content.
What is Google Trends?
Google Trends is a free tool from Google that allows you to analyze search trends. And here a moment of clarification is in order, because trends in Google's tool is not the same as trends in the dictionary sense.
The Cambridge Dictionary states that a trend is ‘a general development or change in a situation or in the way that people are behaving.’
In Google Trends, on the other hand, trends should be understood as interest in a particular topic over time.
By analyzing trends - seasonal, currently popular, or past - you can draw a lot of conclusions, which can be crucial, for example, for planning the publication of articles or for running an efficient marketing campaign.
Using Google Trends, you can find useful statistics on topics that interest you. For example, if you care about swimwear sales, you can access information on when people are most likely to search for them via the Internet.
This way you won't waste sizable amounts of money on promotion during a period when it reaches a negligible audience. Instead, you can check how swimwear-related key phrase searches have performed year after year for the past five years, and take action at the right time of year, minimally outpacing the trend - and the competition.
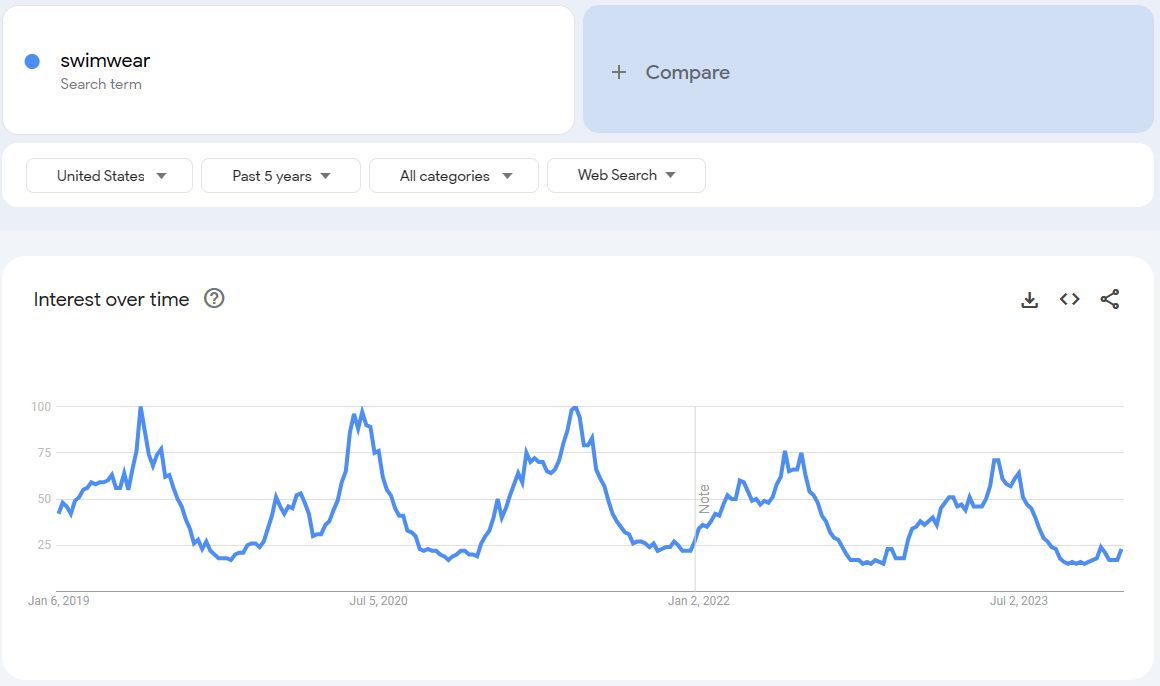
This also works the other way: if you run a general news website, or if it has, for example, a sports section, you can track trends in the whole United States or just the states or counties you are interested in and write about these topics.
Trends are represented by graphs, in which you see increases and decreases in the popularity of certain keywords. However, they are not meant as a total number of searches. Instead, the number is first normalized and then indexed on a scale of 1-100, where 1 means no interest at all and 100 means very high interest. Thus, comparing two keywords might seem pointless, as they would be placed on a completely different scale. Luckily, Google has thought about this, and added the ability to compare keywords with each other, so you can easily find out which one is more popular.
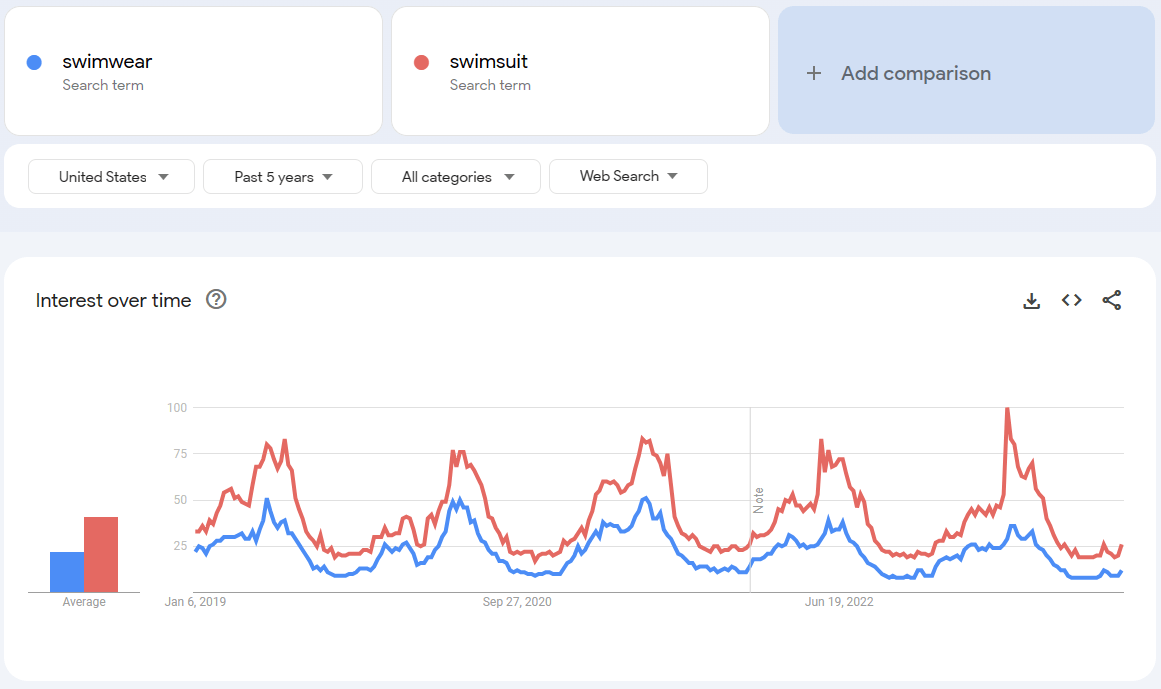
To avoid artificially pumping up the popularity of topics when one user searches for the same keywords multiple times in a short period, they are counted as only one search.
How to use Google Trends?
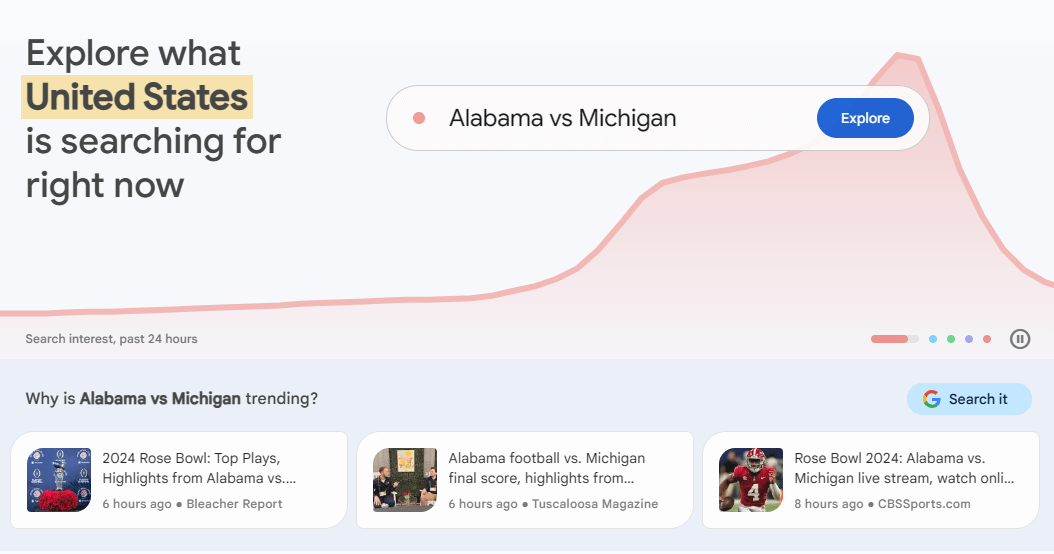
Go to trends.google.com. You’ll see a page like this in the screenshot above. The site immediately suggests the topics that are most popular in a specific location, in this case, the United States of America.
Each of the popular topics suggested on the sliding panel at the top of the page is accompanied by articles with a description justifying the popularity of these topics. Understanding them will allow you to recreate these topics and benefit from their rising popularity.
To see the list of existing trends in detail, go to the Trending Now tab in the upper left corner.
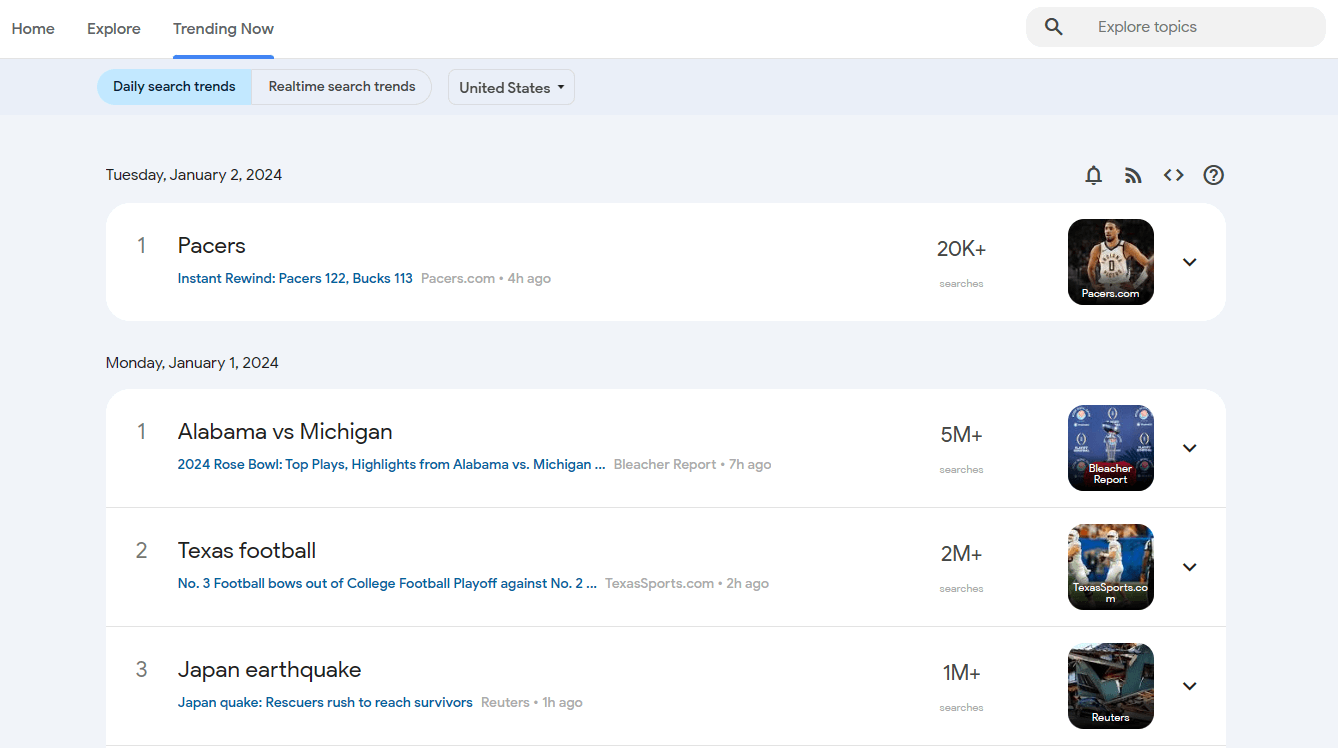
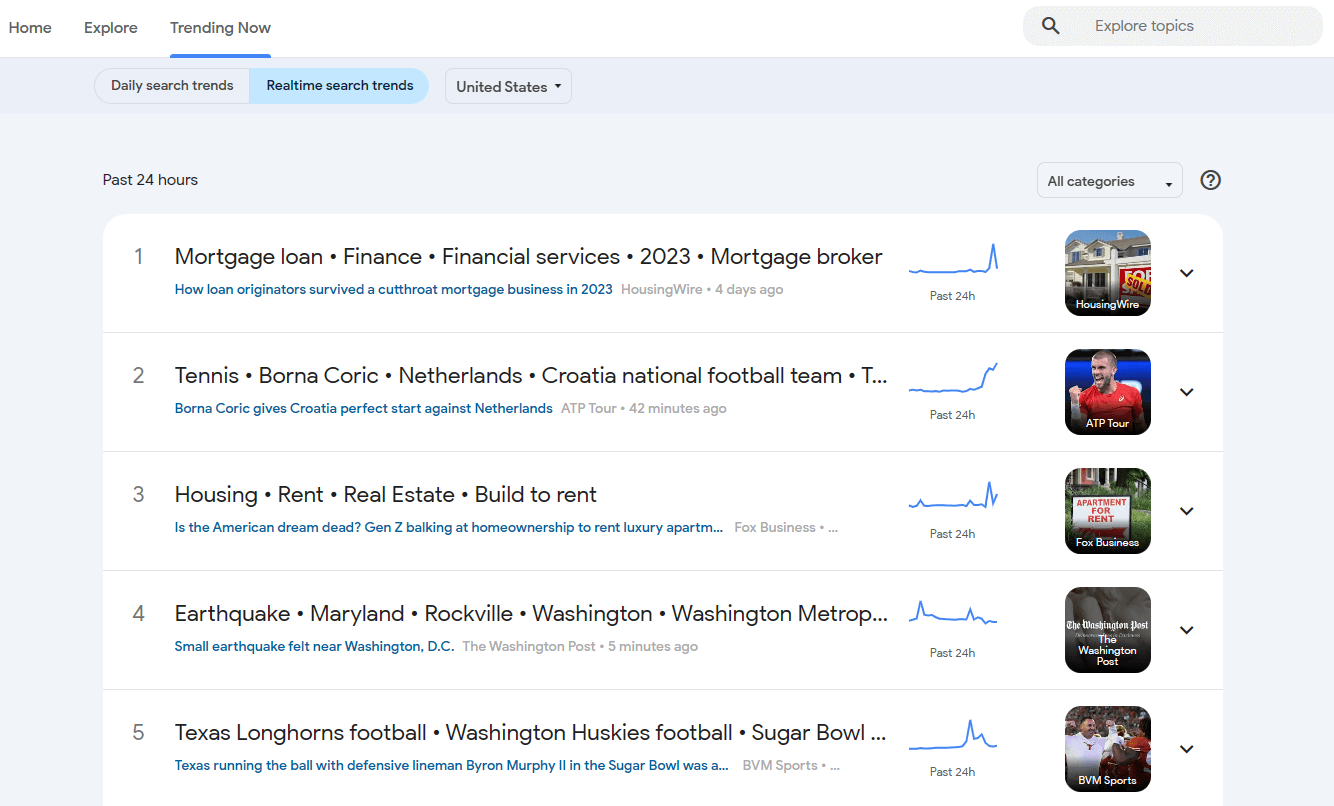
Adjust the timeframe by switching from the "Daily Search Trends" tab to the "Realtime Search Trends" tab. Choose the desired location by selecting one of the available countries.
What's more, by expanding a specific trend using the ‘ ˇ ‘ arrow, you can see not only a list of related articles, but also a list of similar queries. They will help you understand what that trend is all about, what search terms Internet users are looking for, and therefore what to include in your text on that topic in order to reach them.
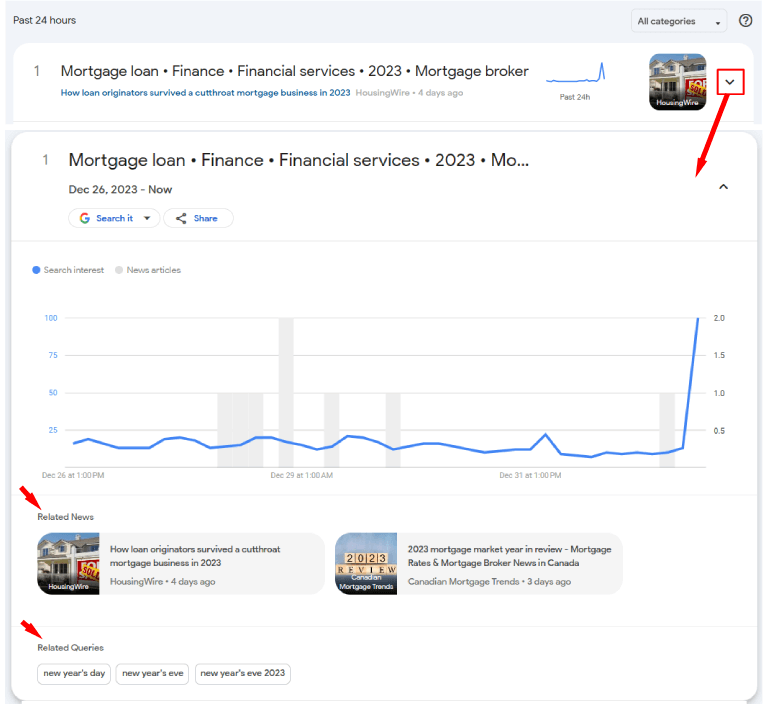
However, this is not the most efficient solution because the same thing is being done by everyone. Instead of joining late to existing trends, it's better to get a little ahead of them. How can this be achieved?
Seasonal trends in Google Trends
As mentioned earlier, there are so-called ‘seasonal trends’. These are phrases that appear among the frequent searches year after year, but not all year round. In the summer, it is unlikely that anyone would want to buy a winter jacket. In winter, on the other hand, no one buys sun hats.
The same applies to various holidays – fireworks are only likely to be purchased before the 4th of July and before New Year’s Eve. Most people will buy turkey before Thanksgiving. And so on. Analyzing the popularity of key phrases during the year on a scale of several years, it is quite safe to conclude. For example, for at least 5 years there has been a growing interest in Halloween costumes in early September.
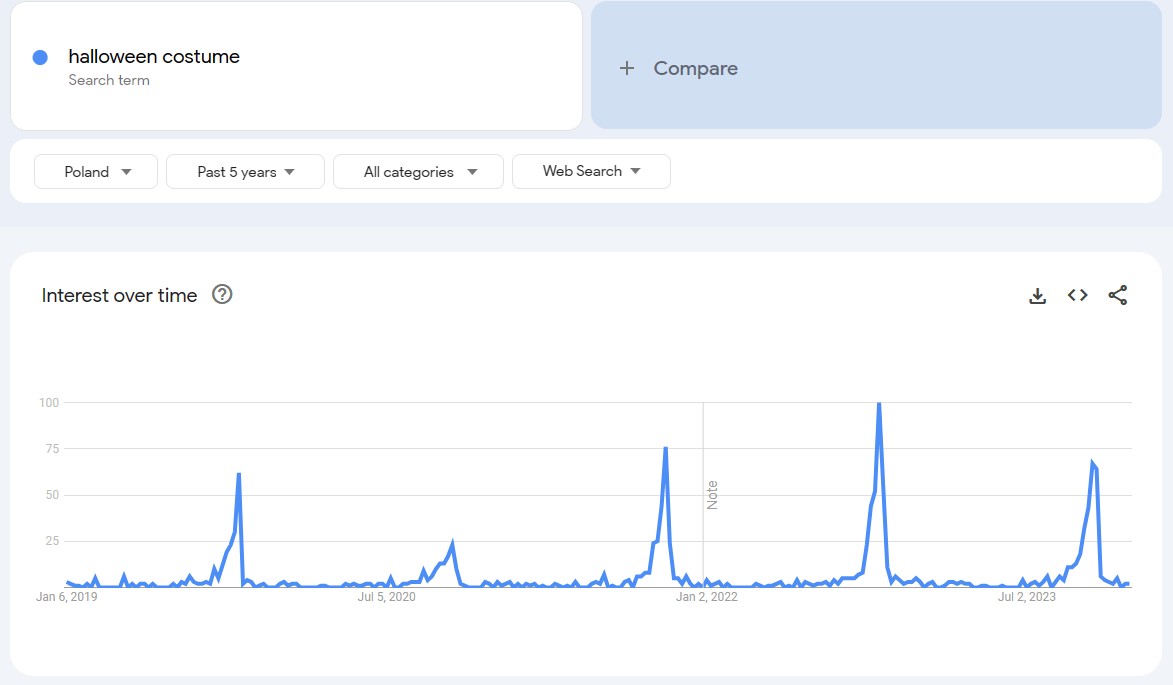
You can draw additional conclusions from these charts. E.g., in 2020, few people were interested in Halloween compared to previous years. In the fall of 2020, Poland was hit by a second wave of coronavirus, and the frightened society was additionally likely to be placed under restrictions. For what it's worth, a year later, when it was possible to leave the house, the quarantine-weary society began to feel a greater need to relax out of home and get together with friends, so the volume of searches around the topic "Halloween costume" exceeded that pre-pandemic.
These conclusions, of course, are not supported by research results, just intuition and deduction. But with the constantly accelerating pace of life, if you want to get ahead of the competition and reach your audience, there is no time to think, only to act. And post Halloween articles as early as the first week of September!
Keep in mind, however, that if the keyword is relatively fresh - for example, a new movie has been announced - the results from previous years will only be misleading. Therefore, in order to reliably use this feature, always do research about the trend beforehand.
The importance of regional language in Google Trends
Despite the fact that, aside from accent, American English is relatively uniform throughout the country, there are some significant differences, visible in regionalisms and words that are in use only in certain areas.
Of course, with the Internet, we’re all becoming more aware of these differences. But even knowing a few phrases meaning the same thing, for example – tennis shoes and sneakers – there is still one I prefer to use and will type in Google.
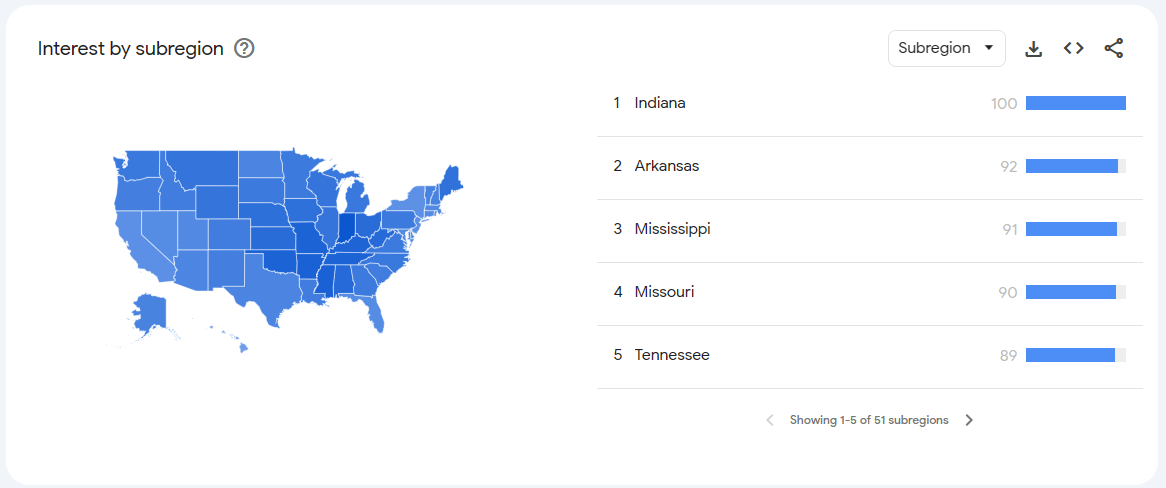
It is important to be aware of which words from our everyday language are commonly known and used in the whole country, and which only function in our environment. Let's take ‘skillet’ as an example.
If someone from the South was to sell skillets to the whole country, he might be clueless as to why the efforts put into promoting his product amount to nothing.
While commonly used in the Midland and South, Northerners prefer the term ‘frying pan’. Hence, they might not Google the term ‘skillet’ while looking for a new frying pan. Luckily, Google has understood the importance of regionalisms and allows you to analyze the popularity of certain terms by state or even city.
By typing in ‘skillet’ and scrolling down, you can see that the term is popular mainly in Indiana state.
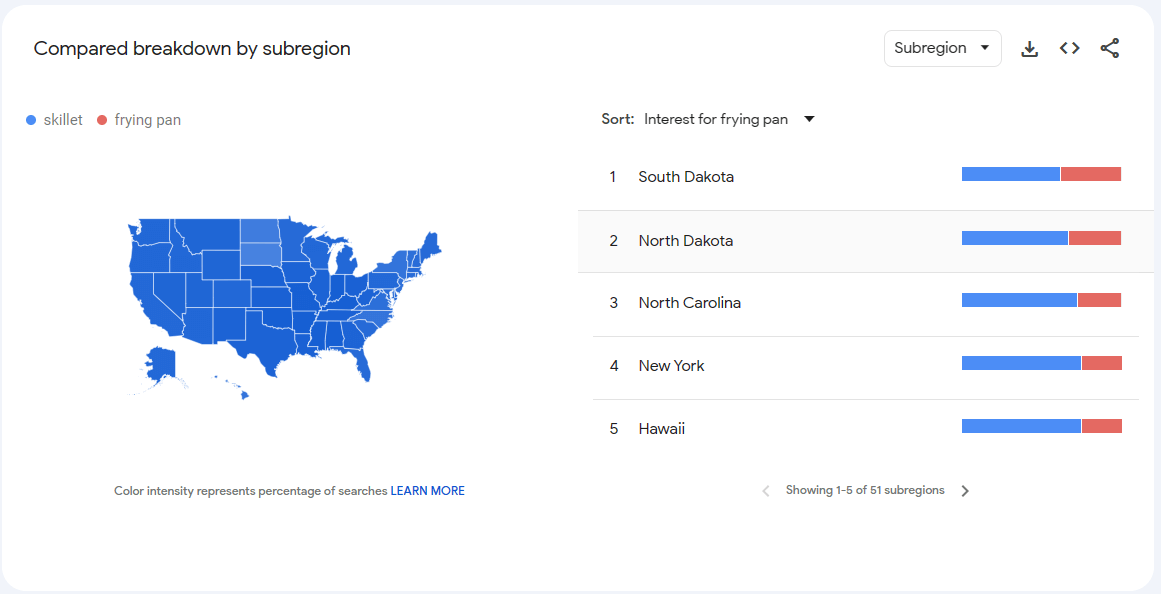
However, you can use the comparison function. Add a second phrase, in this case ‘frying pan’. You’ll immediately see which one is better if you’re planning a nationwide campaign.
How to use Google Trends in a journalist's work?
If you want to stay on top when running a news website that focuses on general topics from different areas, you need to consistently provide your readers with content that draws their attention. Therefore, if you see that in your county, or preferably in the whole country, certain phrases are on a roll - don't wait. You stand a chance of generating a huge number of entries to your website.
How do you find these phrases in Google Trends? The answer lies in a proper analysis of the charts.
To get to them, go into Realtime Search Trends. They are located in the section Trending Now.
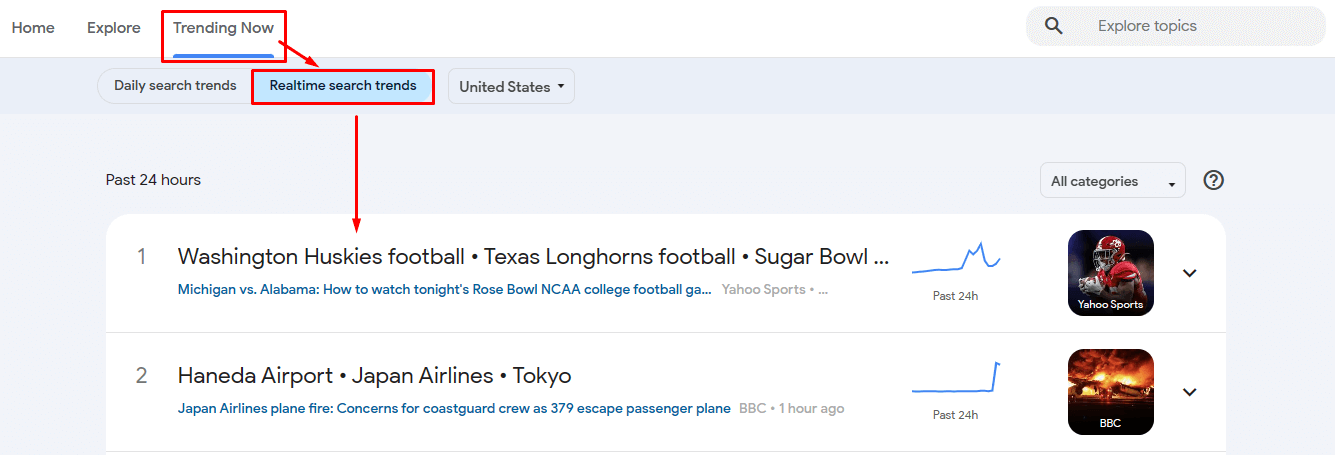
Realtime Search Trends show topics gaining popularity on Google services (including Google Search, YouTube, Google News) in the last 24 hours.
If you see a graph like the one below next to any of the topics and headlines:
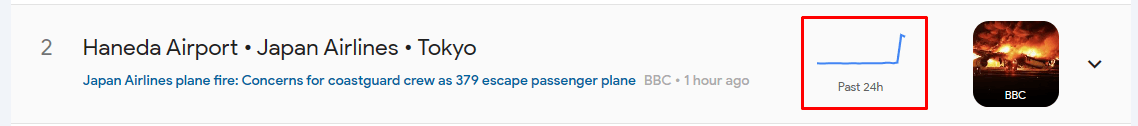
it means, for example, that suddenly some new facts on the topic have come to light or something new has happened and the topic is regaining popularity. This is the last moment for you to publish an article on that topic on the very same day.
To see a detailed hourly chart, click on the arrow in the upper right corner of the photo.
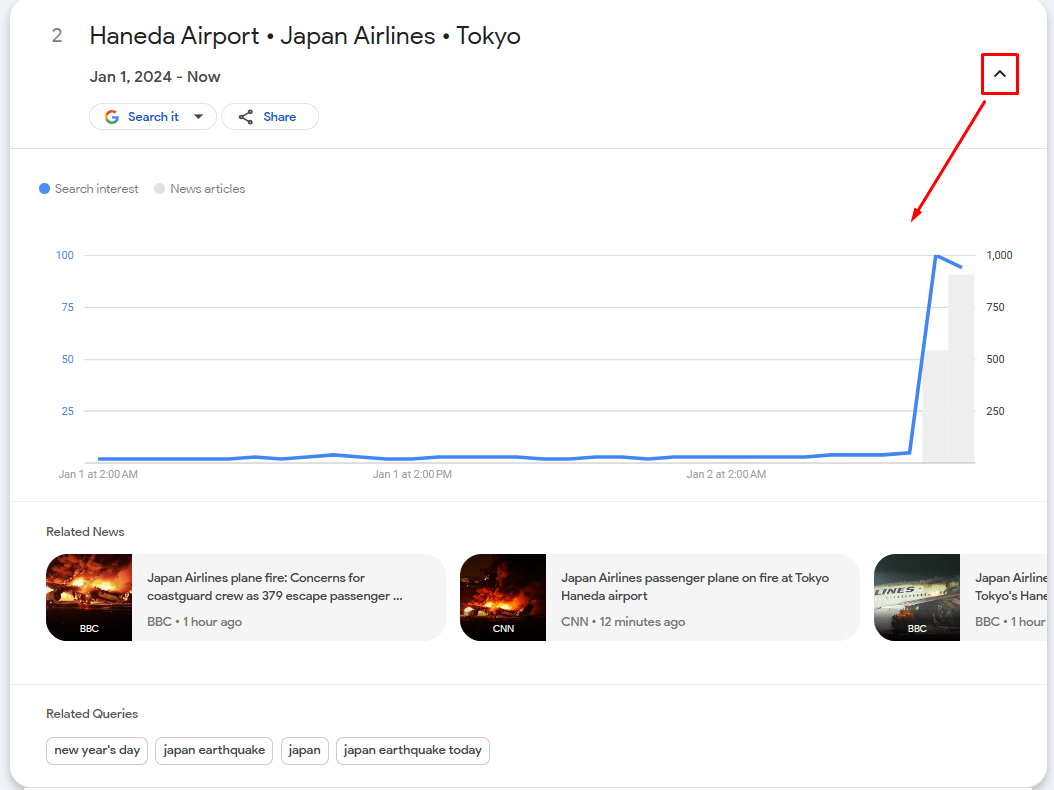
The chart clearly shows that in the last hour, the interest has increased significantly. This is precisely the sign for a journalist that the topic needs to be covered immediately!
Under the chart, related news will also be displayed, which the journalist should review to get an idea of what has already been written on the topic and what hasn’t.
Attention should also be paid to Related Queries. Some of them can be used when writing an article, for example, in headlines or as additional paragraphs.
The main phrases that a journalist should use in the article title / H2 headline in the above example will be the topics highlighted by Google, such as “Japan earthquake”.
But simply writing an article on a trending topic in the last 24 hours is not enough.
Immediately after publication, it is worth seeing to it that the article is quickly added to Google's index, which can be reported in Google Search Console.
By writing articles on trending topics using Google Trends, you increase your chances of:
- increasing net traffic and clicks from social media on a trending topic,
- gaining in the eyes of your audience, because you are not just writing about local accidents and crime stories. Making a national topic feel somehow local will grant you even bigger benefits,
- appearing in Google News, e.g. in the For You or Picks For You.
Summary
Analyzing trends: seasonal, emerging, and declining, it is easy to conclude what is worth writing about, and which topics seem to have exhausted their usefulness.
Google Trends can be a remedy for the lack of creative vigor, which, unfortunately, is an issue for many journalists. When they have no idea what to write about, show them this tool. It might just be a breath of fresh air they need. And it will further maximize the chance of a large number of your webpage views.
Remember, however, that when applying for trends, patience may be necessary to see results. Rome wasn’t built in a day!



